This section gives an overview of ISO's scientific capabilities. It serves as a guideline to the proposer to make a first selection on which capability of which instrument will be most suitable for the proposer's scientific case.
The capabilities provided by the spacecraft are:
Observations can be carried out at one single position - single pointing - or in a series of sky positions arranged in a regular grid, where the observation is repeated at each position - raster map. Slewing is only used for initial target acquisition and to move the spacecraft to the next raster map point. The spacecraft observing modes are explained in detail in Part III.
ISO's payload consists of four instruments:
The capabilities provided jointly by these instruments can be summarized in the following categories:
Direct IMAGING is achieved by using arrays in broad and narrow spectral
bands across much of the entire wavelength range from 2.5 to 240 ![]() m
with CAM and PHT. Imaging can be performed on a single position or in a
raster map. Spatial oversampling is possible. Table 3
summarizes the imaging capabilities including the available pixel
fields of view. Images can also be constructed, e.g. in the wavelength
range from 18 to 50
m
with CAM and PHT. Imaging can be performed on a single position or in a
raster map. Spatial oversampling is possible. Table 3
summarizes the imaging capabilities including the available pixel
fields of view. Images can also be constructed, e.g. in the wavelength
range from 18 to 50 ![]() m, with a single detector when used in raster
mode (Sect. 13.3). Naturally, the efficiency of a single
detector raster mapping is much lower than with an array even when the
array is small as is the case in the far infrared.
m, with a single detector when used in raster
mode (Sect. 13.3). Naturally, the efficiency of a single
detector raster mapping is much lower than with an array even when the
array is small as is the case in the far infrared.
|
Wavelength Range [ | Instrument | No. of Pixels | Pixel field of view [''] |
| 2.5 - 5 | CAM | 32 | 1.5, 3, 6, 12 |
| 5 - 17 | CAM | 32 | 1.5, 3, 6, 12 |
| 50 - 120 | PHT | 3 | 43.5 |
| 120 - 240 | PHT | 2 | 89.4 |
PHOTOMETRY and POLARIMETRY can be achieved in broad and narrow spectral
bands across the entire wavelength range with CAM and PHT. Observations
using multiple apertures can be performed out to 125 ![]() m. Both
instruments are equipped with three polarizers which can be used with
various pixel fields of view (CAM) or spectral band/aperture
combinations (PHT). Photometry and polarimetry can be made on a single
position or in a raster map. Additionally, a sparse map, that is a map with
arbitrarily spaced pointings within a given area, can be obtained with PHT.
m. Both
instruments are equipped with three polarizers which can be used with
various pixel fields of view (CAM) or spectral band/aperture
combinations (PHT). Photometry and polarimetry can be made on a single
position or in a raster map. Additionally, a sparse map, that is a map with
arbitrarily spaced pointings within a given area, can be obtained with PHT.
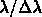 .
.For SPECTROSCOPY, resolving powers from 40 to 20,000 are available (see Table 4). The sampling of the spectra depends on the instrument. LWS has a number of single detectors each one dedicated to a specific wavelength range. Within a wavelength range a spectrum is obtained spectral point by spectral point. SWS has a number of linear detector arrays, where each samples a small portion of the spectrum - a subspectrum - which has a length of eight resolution elements. The spectrum in the required wavelength range is obtained by observing the appropriate number of overlapping subspectra.
Spectrophotometry can be carried out with the PHT-S subinstrument, where the entire spectrum is obtained simultaneously, or with CAM which uses a Circular Variable Filter (CVF) and where spectral images are taken at one CVF position at a time.
Spectroscopic and spectrophotometric observations can be made on a single position or in a raster map.
|
Wavelength Range [ | Instrument | Resolution | Optical Element |
| | |||
| 2.5 - 12 | PHT-S | 90 | Grating |
| 2.5 - 17 | CAM | 40 | Circular Variable Filter |
| 2.5 - 45 | SWS | 2000 | Grating |
| 15 - 35 | SWS | 20000 | Grating + Fabry-Pérot |
| 43 - 197.6 | LWS | 200 | Grating |
| 43 - 197.6 | LWS | 15000 | Grating + Fabry-Pérot |